Genetic Testing
Cogentech offers genetic testing for the assessment of cancer risk using two propriety NGS Panels, OncoPan® for the most common adult hereditary cancer syndromes and OncoPed® for pediatric and rare hereditary cancer syndromes. OncoPan® assesses not only the presence of pathogenic variants in 42 cancer predisposing genes but also 313 SNP for the calculation of the polygenic risk score for Breast and ovarian cancer.
In addition, mutation testing in relatives to identify potential mutation carriers is performed using Sanger Sequencing and MLPA analysis.
Testing is generally performed on blood samples but can also be done on buccal smears.
Personalized medicine
Cogentech’s propriety OncoPan® besides assessing cancer risk, is also designed to help to direct therapy with PARP inhibitors:
- BRCA1/2 somatic testing for therapy with PARP inhibitors in breast, ovarian, prostate and pancreas cancer
- As OncoHRD for therapy with PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer
- Mutation analysis of the most frequently mutated cancer genes
Testing is generally performed on FFPE tumor samples.
Hereditary Tumor Testing
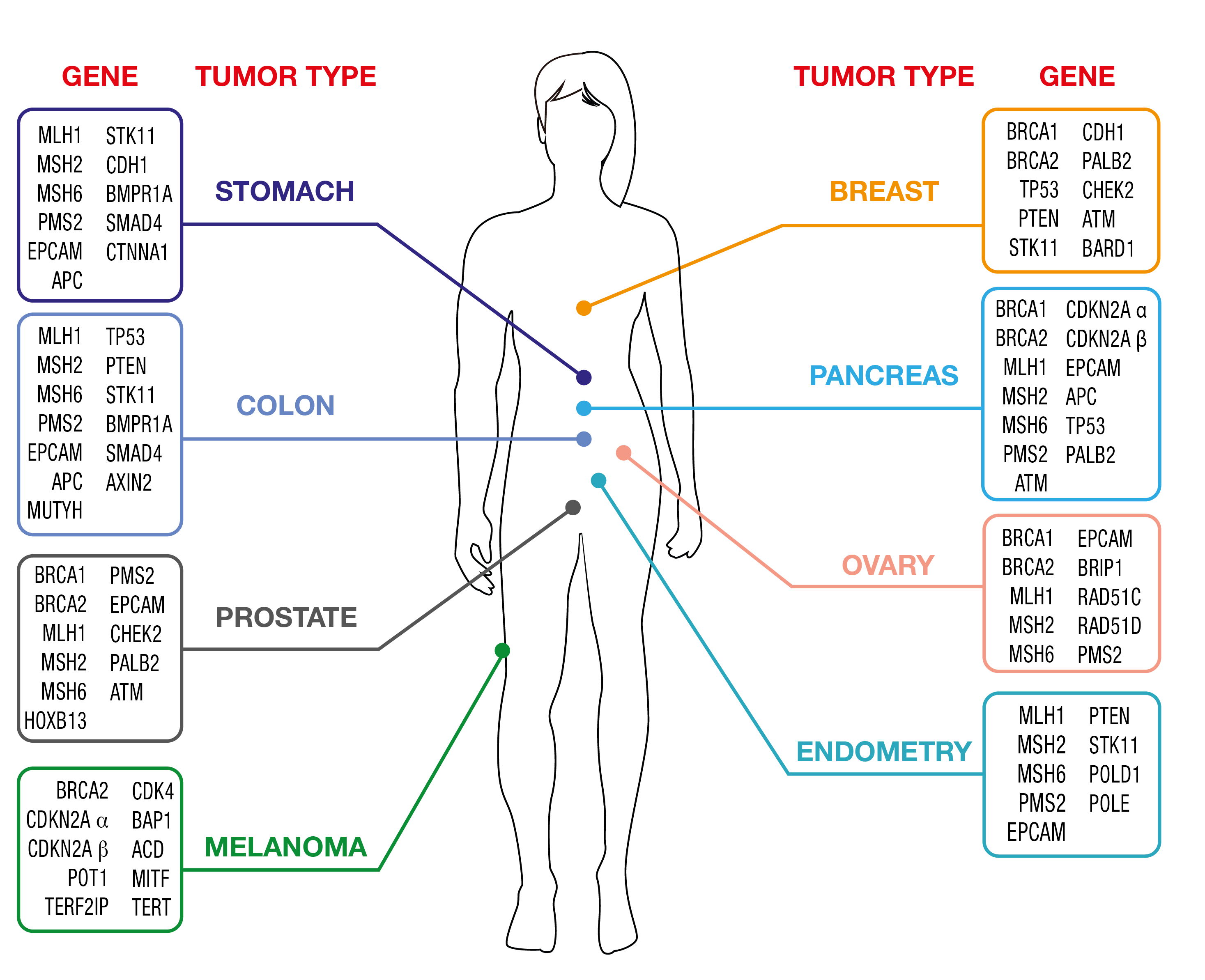
OncoPan® Adult Hereditary Cancer Syndromes
Cancer diagnostics is a fast-paced field and hereditary tumors are not an exception. OncoPan® responds to fast changing needs being an innovative and modular NGS panel that covers 52 genes and an additional 313 SNP for the calculation of a Polygenic Risk Score (PRS). Clinicians can request restricted panels for genetic testing that can be integrated by the analysis of further genes included in OncoPan® if the initial analysis did not provide a diagnostic resolution. This approach reduces costs and diagnosis time, while improving detection rates. In addition, the PRS score will be made available and might be used by the Clinician to optimize the determination of the cancer risk using dedicated web-based tools (www.canrisk.org).
OncoPan® is, based on the frequency that these syndromes occur in the general population, mainly used for genetic testing of Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) and Colorectal Cancer Syndromes.
Click here for detailed list of Hereditary Cancer Syndromes and genes that are covered by OncoPan®
Click here for the technical data sheet for OncoPan®.
Women carrying pathogenic variants in BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, have an overall risk of roughly 70% of developing breast cancer over the course of their life, an increased risk for contralateral breast cancer and for ovarian cancer. Male carriers are particularly exposed to prostate cancer with some risk for male breast cancer. Scientific evidence shows also an increased risk for other types of neoplasms, such as melanoma, stomach cancer, pancreatic and bile ducts cancer.
| Hereditary Cancer associated with mutations in BRCA1/2 | % risk associated with | |
|---|---|---|
| BRCA1 | BRCA2 | |
| Breast cancer | 72 | 69 |
| Contralateral breast cancer | 40 | 26 |
| Ovarian cancer | 44 | 17 |
| Male breast cancer | 1-5 | 5-10 |
| Prostate cancer | - | 27 |
A small percentage of hereditary breast cancers is linked to the presence of variants in other genes, such as PALB2, TP53, PTEN, STK11, CDH1. For these genes, the risk of developing breast tumors is still high, ranging from 35% to 60%, varying from gene to gene. Some of them are associated with specific genetic syndromes that predispose to a variety of well-defined neoplasms.
An increased risk of ovarian tumor, around 15%, may be due to the presence of variants in genes such as RAD51C, RAD51D, BRIP1. Also, variations in the Mismatch Repair genes (MMR), i.e., MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 and large deletions of the EPCAM gene, which predispose to the onset of colon tumors associated with Lynch Syndrome, can confer susceptibility to ovarian carcinoma with associated risks of 10%-17%.
Finally, genes have been identified that confer a moderate-mild risk of developing breast tumors (ATM, CHEK2, BARD1) and several hundred nucleotide variations (SNPs) whose combined effect (Polygenic risk score, PRS) can modulate the risk conferred by the major susceptibility genes BRCA1, BRCA2 , PALB2, ATM e CHEK2.
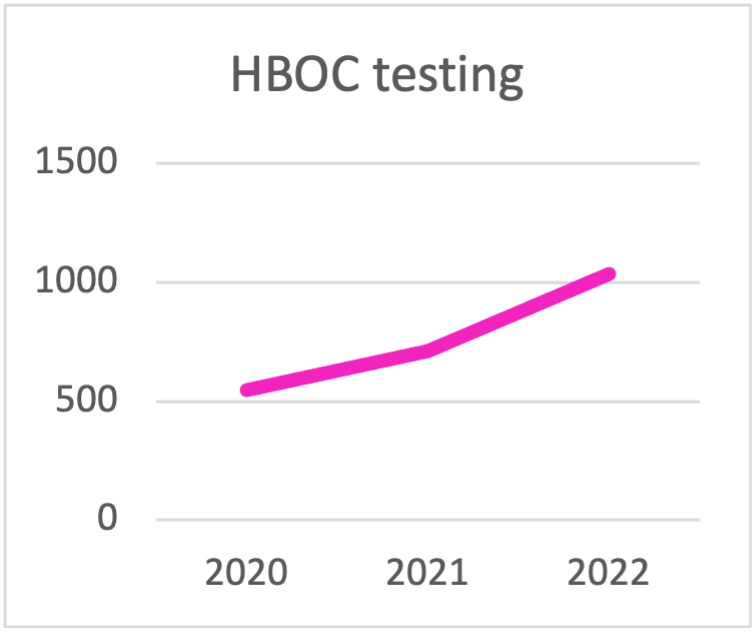
In recent years testing for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) has been increasing reflecting the fact that more hospitals initiated to provide testing to their patients.
In addition, the trend to replace BRCA1/2 only testing with expanded testing panels to permit better diagnosis, is also evident. This is due to the fact that while these forms of predisposition generally have specific clinical manifestations, in some cases, they are not well-defined and can overlap to some extent. The introduction of multigene panels in Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) such as OncoPan® enables a "one-step" approach, particularly useful in cases of genetic heterogeneity.
| HBOC testing | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BRCA | 445 | 313 | 290 |
| BRCA1/2 + PALB2 | 89 | 227 | 301 |
| > 10 gene panel for HBOC | 14 | 170 | 445 |
| TOTAL HBOC TESTING | 548 | 710 | 1036 |
Panel choice for HBOC testing during the last triennial.
The trend is towards testing with panels that contain
more than 10 genes.
OncoPan® has incorporated 313 SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) for the calculation of the PRS Z-score with a dedicated algorithm that Cogentech has implemented. Polygenic Risk Scores are an important component of breast cancer risk prediction and explain over 30% of heritable breast cancer. Polygenic Risk Scores are based on the combined result of common genetic variants. With a dedicated software (www.canrisk.org) a medical professional can use the PRS to better calculate the risks of developing breast and ovarian cancer in women by integrating also other risk factors such as lifestyle, genetic test results and family history. Currently, the PRS for breast and ovarian cancer has been validated in European cohorts only and further testing for different ancestries is needed and ongoing.
The most common hereditary predispositions to develop colorectal tumors are Lynch syndrome, caused by alterations in the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, EPCAM genes, and Familial Polyposis, predominantly caused by mutations in the APC and MUTYH genes. Additionally, the genes SMAD4 and BMPR1A are associated with the onset of Juvenile Polyposis. Recently, new predisposition genes for polyposis and colon tumors have been identified: POLE and POLD1 (polyposis associated with mutations in the exonuclease domains of DNA polymerases), NTHL1, MSH3 and AXIN2. Forms of colon polyps and adenomas are also present in patients with Cowden syndrome, caused by variants in the PTEN gene, or with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, caused by variants in the STK11 gene. Diffuse-type gastric tumors can be due to germline mutations in the CDH1 gene. Recently, a new predisposition gene, CTNNA1, has been identified, which has been reported in few cases so far but should be considered for risk assessment.
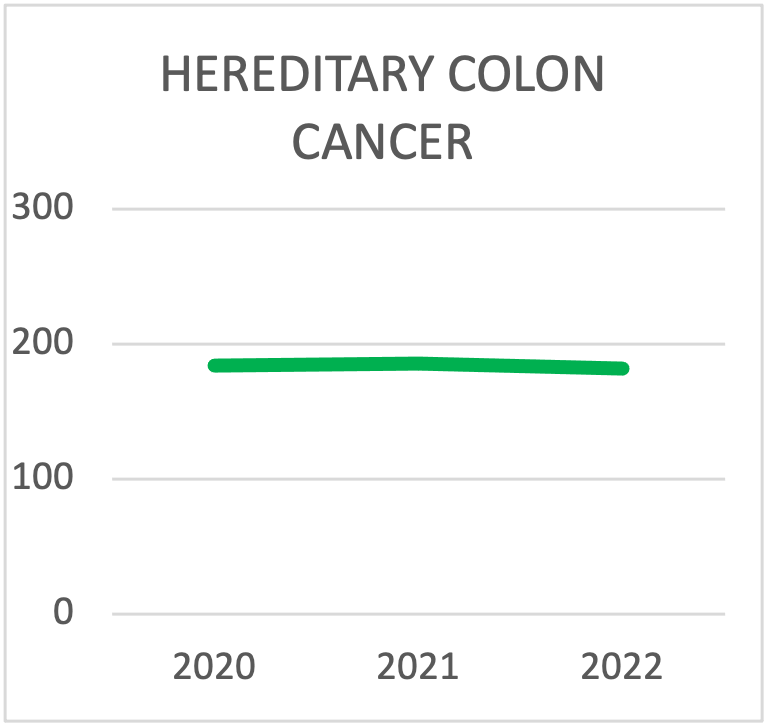
These forms of predisposition generally have specific clinical manifestations. However, in some cases, they are not well-defined and can overlap to some extent. Indeed, based on literature data, it is increasingly evident that analyzing only the most indicative genes for each condition can be limiting. The introduction of multigene panels in Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) enables a "one-step" approach, particularly useful in cases of genetic heterogeneity. This approach reduces costs and diagnosis time, while improving detection rates. In conclusion, comprehensive analysis using multi-gene panels can provide more informative results in terms of the percentage of patients eligible for surveillance or therapy. That is why they are widely used in diagnostic settings.
| HEREDITARY COLON CANCER SYNDROMES TESTING | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lynch | 123 | 131 | 113 |
| FAP | 42 | 30 | 22 |
| > 10 gene panel for colon | 19 | 25 | 47 |
| TOTAL TESTING | 184 | 186 | 182 |
Panel choice for Hereditary Colon Cancer Syndrome testing during the last triennial. The trend is towards testing with panels that contain more than 10 genes.
Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant cancer syndrome associated with a genetic predisposition to different cancer types. It is also known as Hereditary Non-Polyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC). Lynch syndrome is among the most common hereditary cancer syndromes with an estimated prevalence of 0.3% in the general population. Diagnoses of colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, and/or other cancers in multiple relatives on the same side of a family and a young age at diagnosis might indicate Lynch Syndrome. People with Lynch syndrome might develop multiple types of cancers during their lifetime. Currently, testing for Lynch Syndrome involves the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 and EPCAM genes.
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant disease that consists of the development of hundreds or even thousands of polyps in the mucous membrane of the colon as early as puberty. Polyps are present in 50% of patients by the age of 15 and 95% by the age of 35. Cancer develops before the age of 40 in almost all untreated patients. Patients may also develop extracolonic manifestations i.e. desmoid tumors, osteomas of the skull or jaw, sebaceous cysts and adenomas in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Patients have an increased risk of cancer in the duodenum, pancreas, thyroid, medulloblastomas and hepatoblastoma in children. In most cases FAP is linked to the germline mutation of the APC gene.
MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP) is an autosomal recessive disease and develops in adulthood. MAP often presents with an attenuated phenotype i.e., the development of a few dozen colorectal polyps, which may evolve into colon carcinomas, and is due to biallelic mutations in the MUTYH gene.
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome (LFS) is a hereditary cancer predisposition syndrome caused by a mutation in p53, a tumor suppressor gene. The Syndrome takes its name from Dr. Li and Dr. Fraumeni who first described the disease in 1969. Affected patients tend to be of young age, with half of the affected individuals receiving the first diagnosis before the age of 30. The most common tumors that develop in affected patients are osteosarcoma, soft tissue sarcoma, acute leukemia, breast cancer, brain cancer, adrenal cortical tumors, and a variety of other tumors less frequently. The lifetime risk for a person affected by LFS to develop a cancer is 90% that is why it is important to have an effective screening protocol in place.
Cowden Syndrome (CS) is part of hamartoma tumor syndrome caused by mutations in PTEN. Cowden syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant condition that brings a 50-85% lifetime risk for female patients to develop breast cancer. Other cancer types carry a smaller risk such as thyroid cancer (30-40%), kidney cancer (30-35%), endometrial cancer (25-30%), colorectal cancer (5-10%) and melanoma (6%).
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) is caused by mutations in STK11, a tumor suppressor gene. PHS is a rare autosomal dominant disorder that causes the growth of hamartomatous polyps in the digestive tract in affected patients generally by the age of 10. Complications of these extensive benign growths might be bleeding or intestinal blockage. The lifetime risk of a person with PJS to develop cancer is 93%. The highest risk is for breast cancer (30-50%) followed by colorectal cancer (40%), pancreatic cancer (10-35%), stomach cancer (30%), ovarian cancer (20%), lung cancer (15%) and a variety of other cancers at lower risk.
Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer (HDGC) is a rare inherited condition in which individuals are at an increased risk of developing diffuse gastric cancer and lobular breast cancer. Approximately 20% of all stomach cancers are diffuse gastric cancers, and a small number of these are due to HDGC. Stomach cancers are defined diffuse when they involve most of the stomach, causing thickening of the wall of the stomach instead of staying in one area and forming a distinct mass. The gene involved in HDGC is CDH1, although also CTNNA1 has been shown to be mutated in some cases.
Five to twelve percent of all cutaneous melanoma cases belong to either melanoma-prone families or families with melanoma-related multicancer clustering, caused by high and intermediate penetrance alleles in known predisposition genes such as CDKN2A, CDK4, POT1, BAP1, TERT, ACD, TERF2IP, MITF e ATM. CDKN2A and CDK4 are high-penetrance genes associated with an increased risk of familial melanoma. The prevalence of pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in the CDKN2A gene is roughly 33% and up to 58% in multiple primary melanoma cases.
BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome is an inherited disorder that increases the risk of a variety of benign and cancerous tumors, most commonly certain types of tumors that occur in the skin, eyes, kidneys, and the mesothelium. Affected individuals can develop one or more types of tumors, and affected members of the same family can have different types. BAP1-TPDS is caused by germline mutations in the BAP1 gene. The most common tumors are uveal melanoma, malignant mesothelioma and clear cell renal carcinoma.
OncoPed® - Pediatric tumors and rare genetic cancer syndromes
OncoPed® is indicated for the analysis of genes conferring susceptibility to tumors that develop predominantly in pediatric age and for the evaluation of rare syndromic conditions that may also develop in adulthood (e.g., melanomas and renal neoplasms).
The underlying cause of most pediatric cancers is currently unknown. However, it has been estimated that genetic alterations, responsible for increased susceptibility to tumor development, are present in approximately 8% of pediatric patients and this in the absence of any significant family history.
OncoPed® provides analysis for genes involved in the most aggressive pediatric cancers such as medulloblastoma, Wilms tumor, some rare ovarian tumors (Sertoly-Leydig and SCCOTH), retinoblastoma, uveal melanoma/melanoma, renal tumors, some lymphomas, rhabdoid tumors as well as tumors developing in Li Fraumeni, Cowden, Gorlin, DICER1 and Carney syndromes. Some of the genes present in Oncopan® are also present in OncoPed®, either because the Syndrome involved presents itself both in young as well as in adult or because of a heterogenous presentation of the cancer phenotype. Syndromes for which testing is unique with OncoPed® are listed below.
Click here for detailed list of the Pediatric and Rare Cancer Syndromes and genes that are covered by OncoPed®.
Click here for the technical data sheet for OncoPed®.
Biallelic mutations in the genes MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 and EPCAM that are involved in Lynch Syndrome, can cause Constitutional Mismatch Repair Deficiency Syndrome (CMMRD). CMMRD is a rare inherited disease that predisposes to malignant tumors with onset in childhood, usually brain cancer, hematological and gastrointestinal cancer.
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma (NBCCS) syndrome also known as Gorlin Syndrome, is a multisystem inherited disease that causes developmental abnormalities and predisposition to certain tumors such as basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and more rarely childhood medulloblastomas. Up to 85% of cases are due to mutations (pathogenic variants) in the PTCH1 gene. More recently, a similar phenotype has been found in association with mutations in SUFU3. Individuals that carry a mutation in either of these two genes are especially sensitive to sun exposure, and might develop thousands of basal cell cancers in the exposed skin area. The lifetime risk of developing BCC in individuals carrying a mutation in PTCH1 is 90%. Drugs blocking the defective pathway caused by mutations in PTCH1 are available and might be prescribed for cancer that has spread or cannot be treated by surgery or radiation therapy.
DICER1 syndrome, caused by mutations in the gene DICER1, is a rare condition that predisposes to various benign and malignant tumors that occur mainly in children and adolescents and damage multiple organs such as lung, kidney, thyroid, ovaries and several other locations in the body: o Pleuropulmonary blastoma (PPB), a cystic lung tumor that may transform into an invasive lung tumor, represents the most dangerous manifestation. o Multinodular goiter (MNG) a benign thyroid condition, and less common, thyroid cancer. o Ovarian tumors (Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor, sarcoma and gynandroblastoma). o Cystic nephroma, a benign kidney tumor, and less common, Wilms’ tumor. o Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the uterine cervix (and less common, other locations).
Retinoblastoma is an eye cancer that develops from retinal cells and almost exclusively affects children under the age of 4-5 years. Retinoblastomas exist in hereditary and sporadic forms. In both cases, a mutation in the Rb1 gene is involved. The disease can present unilateral or bilateral. In 60%- 80% of all cases where the disease presents on both eyes and in 15% of unilateral presentation, a germline mutation in Rb1 has been detected.
Carney Complex (CNC) is a very rare autosomal dominant condition caused by mutations in PRKAR1A, that leads to skin pigmentation anomalies. Endocrine alterations might manifest as acromegaly, thyroid and testicular tumors, and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-independent Cushing's syndrome due to primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease (PPNAD). In addition, myxomas might develop in the heart, skin and breast. Cardiac myxomas can develop in any cardiac chamber, may be multiple and might require surgical removal.
Rhabdoid tumor (RT) is an aggressive pediatric soft tissue sarcoma that arises in the kidney, the liver, the central nervous system, the peripheral nerves and all miscellaneous soft-parts throughout the body. RT is caused by biallelic inactivation of SMARCB1 (90% of all cases) or SMARCA4 and in 25% of cases is associated with germline mutations. In one case a germline mutation in FBXW7, tumor suppressor gen,e has been identified. RT usually occurs in infancy or childhood, mostly affecting patients less than 2 years old. In infants less than one year, RT account for roughly 20% of renal cancers, and 15% of soft-part tumors.
Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL) is a hereditary condition associated with tumors arising in multiple organs caused by mutation in the VHL gene. In patients with VHL mutation, hemangioblastoma (blood vessel tumors) develop in the brain, spinal cord, and retina. Persons affected with VHL also have an increased risk of developing clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (pNET) as well as tumors of the adrenal gland or pheochromocytoma.
Nephroblastoma, or Wilms' tumor, is the most common malignant tumor of the kidney in children and is associated with an abnormal proliferation of embryonic kidney-like cells. The tumor can most frequently develop in one kidney only (unilateral), but in some cases it can affect both kidneys (bilateral). In 90% of all cases, it has a sporadic onset and only in a very small percentage of cases can it be hereditary. In at least 20% of hereditary cases Wilms' tumor is caused by mutations in the WT1 gene. In a few cases a germline mutation in FBXW7, a tumor suppressor gene frequently mutated in human tumors, has been identified.
Germline mutations in the FLCN tumor suppressor gene are responsible for Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (BHD), an autosomal dominant inherited disease that predisposes to fibrofolliculomas, lung cysts often causing spontaneous pneumothorax, and an increased risk of developing kidney tumors.
Hereditary Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma (HPRCC) is a familial renal cancer syndrome characterized by a predisposition to the bilateral and multifocal development of papillary renal cell carcinomas type 1. The predisposition is transmitted as an autosomal dominant character with reduced penetrance. The syndrome is associated with germline mutations of the MET protooncogene.
Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell (HLRCC) consists of the presence of multiple cutaneous leiomyomas in different individuals of the same family. Leiomyomas are benign soft tissue neoplasms that originate from smooth muscle. This rare syndrome is usually transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner and may be associated with tumors such as uterine leiomyomas and renal carcinoma. The disease is caused by germline mutations in the fumarate hydratase gene FH.
Mutation Analysis in Relatives
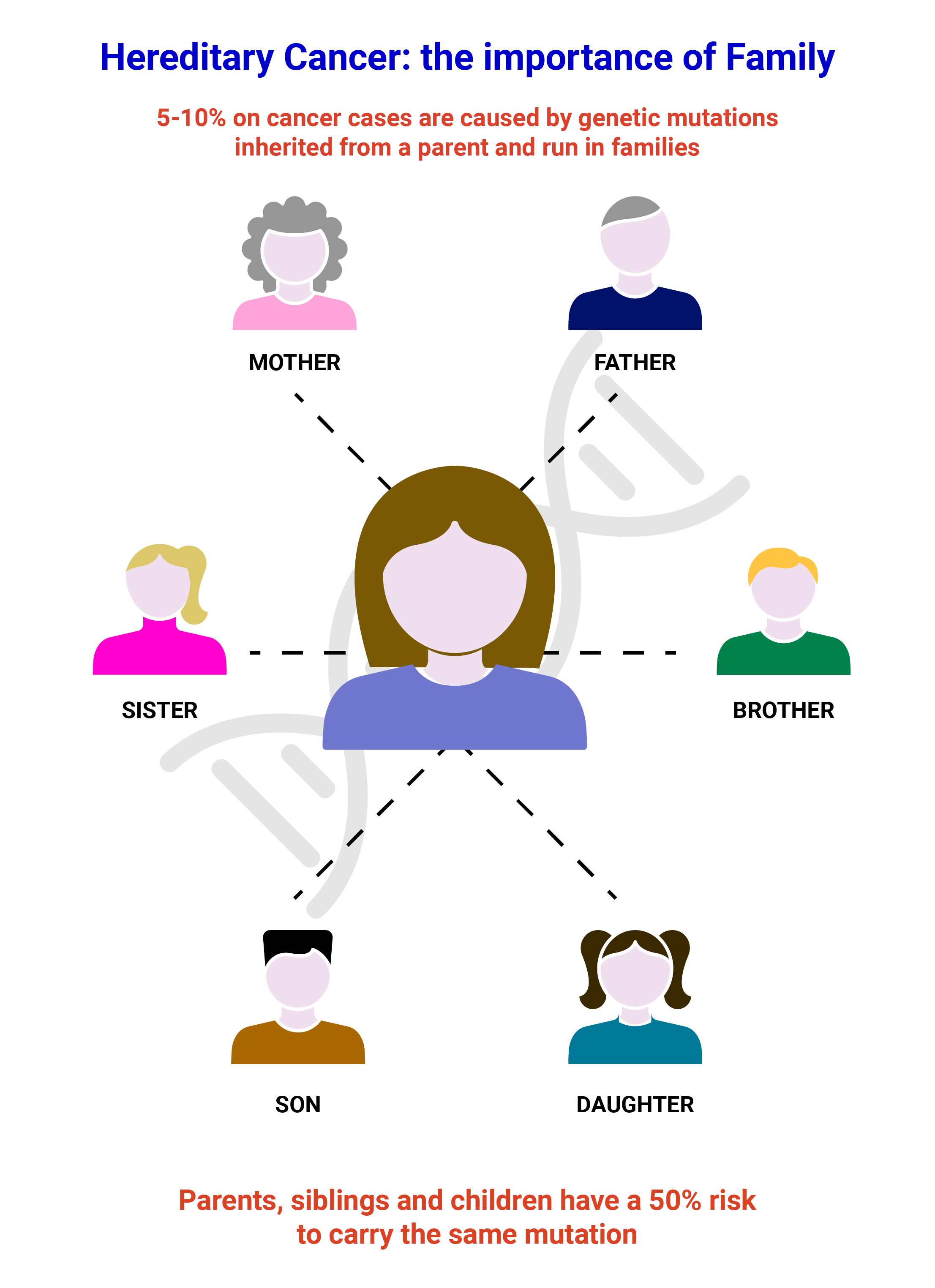
Depending on the kind of mutation identified in the proband, testing of relatives will either be carried out using Sanger Sequencing to verify the presence of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant and small deletions/duplication or with MLPA to identify big deletions or amplifications of a gene. MS-MLPA can also be used to address the methylation status of a gene.
Sanger sequencing is a robust testing strategy able to determine whether a point mutation or small deletion/duplication is present. It is widely used for identifying constitutional (germline) variants in diagnostic testing by reading a small target region of the genome. We carry out Sanger Sequencing using our own, validated primer sets for the validation of variants identified in any of the genes present on our propriety NGS panels and for the testing of relatives.
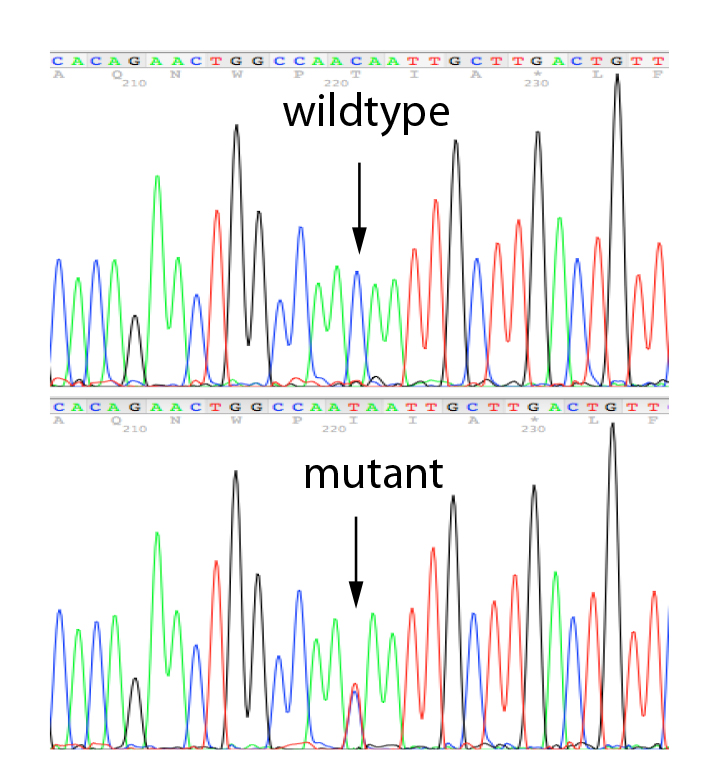
MLPA is a simple, multiplex PCR technique that uses a single primer pair to amplify up to 60 probes, each with a unique genomic target and length. PCR amplicons are fluorescently labelled and separated and quantified by capillary electrophoresis. By comparing the resulting peak pattern of a sample to those of a set of reference samples, the number of genomic targets present in the sample of interest can be determined. MLPA analysis can also be used to determine whether a specific genomic region is methylated (MS-MLPA) which influenced the expression of certain genes. We carry out MLPA for the validation of findings identified in any of the genes present on our propriety NGS panels using Salsa-kits provided by MRC-Holland and for the testing of relatives.
Click here for the technical data sheet for MLPA.
Click here for the technical data sheet for MS-MLPA.
Personalized Therapy
Cogentech’s propriety OncoPan®, besides assessing cancer risk, is also designed to help to direct therapy:
- Somatic BRCA1/2 testing for therapy with PARP inhibitors in breast, ovarian, prostate and pancreas cancer
- As OncoHRD for therapy with PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer (according to European guidelines)
- Mutation analysis of the most frequently mutated cancer genes
PARP inhibitor therapy is based on the fact that a normal cell has two ways of repairing DNA damage: PARP dependent Single-stranded DNA break repair and BRCA1/2 dependent Double-stranded DNA break repair. Upon a single-stranded DNA break the PARP protein binds to the DNA and recruits other proteins which will repair the damage. In the presence of PARP inhibitors, PARP still binds to DNA but can no longer recruit the repair proteins. As a consequence, the damage is not repaired and even worse more DNA damage accumulates in the form of double-stranded DNA breaks. In a normal cell BRCA1/2 depend double-stranded DNA break repair will eliminate the damage and the cell recovers. In a cancer cell that harbors a mutation in BRCA1/, double-stranded DNA breaks can no longer be repaired, thus DNA damage accumulates until the cell can no longer function and dies.
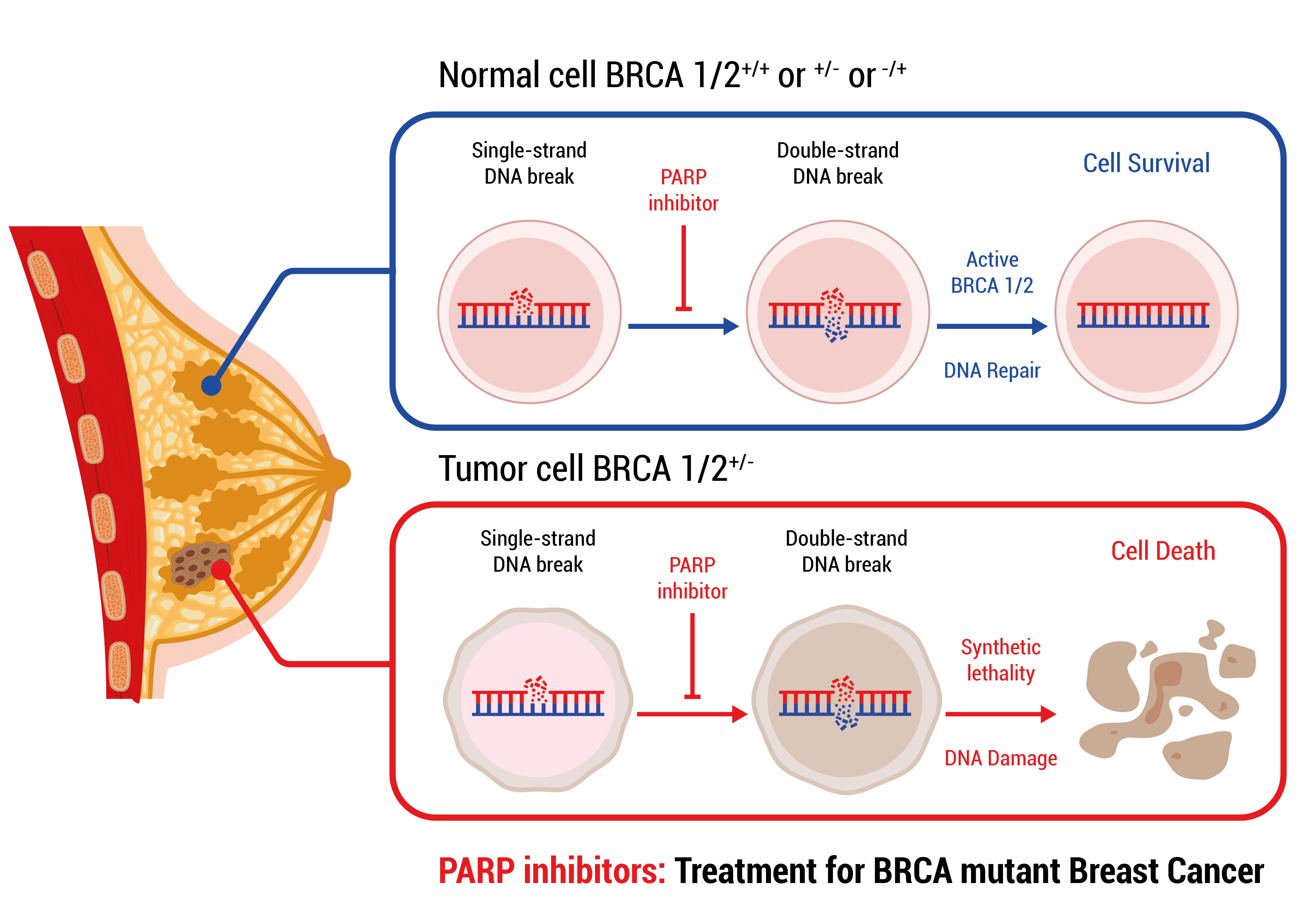
A mutation in BRCA1/2 in a tumor can either be germline or somatic. If prior to the disease germline mutation status has not been assessed, somatic testing, which will reveal both germline and somatic mutations, will be performed to assess eligibility for treatment with PARP inhibitor therapy.
Somatic testing will involve testing for mutations in BRCA1/2 and might be extended to other genes involved in the BRCA1/2 dependent double-stranded DNA repair mechanism to assess for a so-called Homologous Recombination Deficiency or HRD. In the presence of HRD, a specific mutation pattern will be created in the DNA (HRD scar) which can be identified by Whole Genome Sequencing.
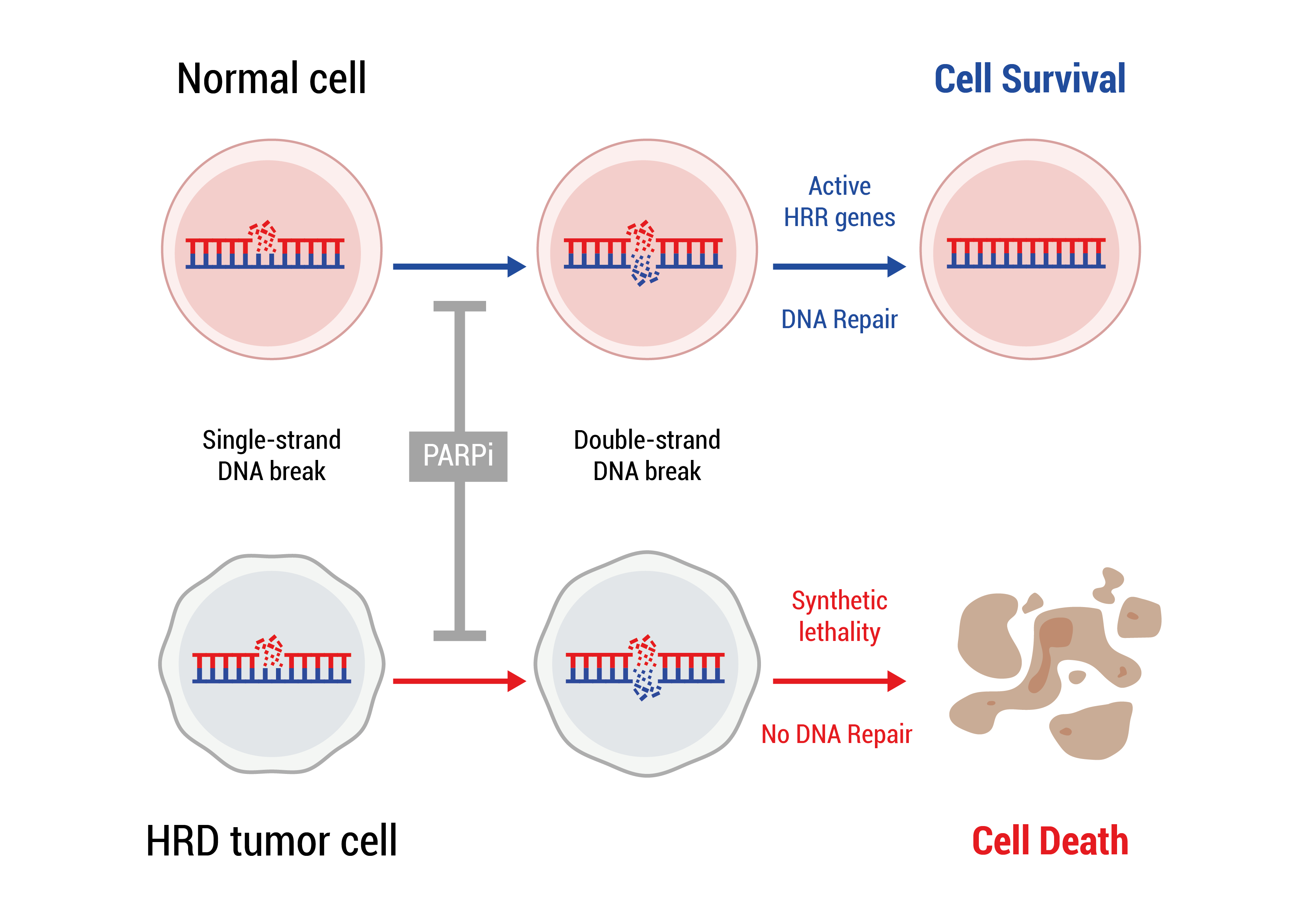
HRD is present in many different cancers. For example, 50% of epithelial ovarian cancers display HRD, but only 15% harbor germline or somatic BRCA1/2 mutations (Konstantinopoulos et al. Cancer Discov 2015;5:1137–54.). Similar numbers are found in triple negative breast cancers with 15% harboring germline BRCA1/2 mutations while an additional 40% of tumors display an HRD scar due to somatic BRCA1/2 mutations or mutations in other genes of the pathway (Grace et al., Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2022, 192, 649-653). In advanced prostate cancers up to 25% of tumors display an HRD scar. (Handy et al., 2018, JCO, 36.15_suppl, 5062)
Currently, according to European guidelines, PARP inhibitor therapy is recommended in as maintenance therapy for ovarian cancer, HER2 negative breast cancer and prostate cancer (for details click here for EMEA, and ESMO). Eligible patients are identified by mutational screening in BRCA1/2 or by testing for HRD (ovarian cancers). Cogentech offers both BRCA1/2 mutation screening and analysis for HRD using its propriety panel OncoPan®.
Mutational analysis of BRCA1/2 using OncoPan® is performed on FFPE tumor samples to identify those patients that might be eligible for therapy with PARP inhibitors.
Click here for the technical data sheet for OncoPan®.
OncoHRD combines the mutational analysis of BRCA1/2 using OncoPan® with a low pass whole genome sequencing (LP-WGS) to verify the presence of HRD using the bioinformatics tool GIInger™ from Sophia Genetics to identify those patients that might be eligible for therapy with PARP inhibitors.
Click here for the technical data sheet for OncoHRD.
The analysis of cancer genes is indicated where it may have therapeutic value, indicating for example sensitivity or resistance to particular drugs, or where it may have prognostic value, giving indications regarding the expected prognosis of the disease.
Colon Cancer
Analysis of KRAS and BRAF is used to evaluate the resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (Cetuximab, Panitumumab) in colon cancer.
Lung Cancer
Analysis of EGFR and NRAS genes assesses sensitivity or resistance to therapies with Gefitinib or Erlotinib in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Melanoma
Mutations in the BRAF gene confer sensitivity to Vemurofenib in metastatic melanoma.
Breast Cancer
Patients with breast cancer may benefit from treatment with Trastuzumab, Lapatinib or Pertuzumab in the presence of HER2 mutations or Alpelisib in combination with Fulvestrant in the presence of PIK3CA mutations.
Gastro-Intestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
Mutations in the c-KIT and PDGFR-α genes are used to confirm the diagnosis of GIST and to assess the risk of progression and resistance to therapy (Imatinib).
Endometrial carcinoma
POLE gene analysis is used for prognostic evaluation in endometrial carcinomas.